

Definition: The events in sequence related to this motor vehicle, regardless of injury and/or property damage. Select up to four events for this vehicle in the order in which they occurred, time wise.
Non-Collision Harmful Events:
Non-Collision events may occur before or after a collision event. They should not be considered separate events if they occur as part of a collision event.Examples:
- A motorcycle strikes a moose, overturns and the rider becomes separated from the vehicle. Select the collision event (11 - Live Animal), not the non-collision (01 –Rollover/ Overturn or 05 - Fell/Jumped from Vehicle) that occur as part of the collision event.
- One tractor/trailer rear-ends another tractor/trailer. The impact pushes the lead vehicle’s load into the back of the tractor cab with part falling onto the roadway. Select the collision event (12 - Motor Vehicle In-Transport), not the non-collision (72 - Cargo/Equipment Loss or Shift) that occurred as part of the collision event.
If there is a 01 – Rollover/Overturn that begins in another location but involves a ditch or embankment in the case (e.g., "rolled through the ditch", "rolled down the embankment", "came to rest against the embankment"), then the rule applies where if there is no damage associated with an impact with the fixed object during the rollover, it is not included in the SEQUENCE OF EVENTS. If there is indication that damage resulted from an impact with the fixed object, it is included in the SEQUENCE OF EVENTS. This follows the same logic as striking a tree or another vehicle during an overturn.
Note: For medium/heavy trucks with attached trailers by fixed ' linkage, when either the power unit or the trailer rolls over, the entire vehicle will be considered a rollover.
For light vehicles, that are not commercial do not select 01 – Rollover/ Overturn if only the trailer portion of the combination overturns.
02 - Fire/Explosion is used for a vehicle fire or explosion that occurs during the crash sequence or as a result of the crash.
As it pertains to the occurrence of 02 - Fire/Explosion, the crash circumstances are not considered stabilized until the threat of damage to this vehicle, or injury consequences to this vehicle's passengers/occupants, has ceased. Therefore, the crash sequence is not considered stabilized until all passengers/occupants have exited the vehicle and the scene has been declared safe. Fires that occur at a later time to vehicles abandoned at the scene (e.g., in open fields, on hillsides, etc.) or to vehicles removed from the scene to another location (tow yard, curbside, etc.) are not considered part of the crash sequence.
03 - Immersion, Full or Partial is used when an in-transport motor vehicle enters a body of water and results in injury or damage.
04 - Gas Inhalation includes injury or death as a result of toxic fumes, such as carbon monoxide fumes leaking from a motor vehicle in-transport.
05 - Fell/Jumped from Vehicle is used when a passenger/occupant of this vehicle falls or jumps (not suicide) from the vehicle causing injury. For example, a passenger of a motor vehicle in-transport leans against the car door, it opens and the passenger falls out; or a person riding on a vehicle’s exterior (hood, roof, running board, etc.) falls or jumps, and is injured by the fall. If a passenger falls or jumps from a vehicle and is struck by that vehicle, use this option.
06 - Injured in Vehicle (Non-Collision) is used when a passenger is injured during an unstabilized situation (see definition for unstabilized situation in Appendix C) without a collision, excluding cargo/equipment loss or shift. Examples: Driver slams on brake, causing an unrestrained passenger to be injured. Driver makes a sharp turn causing driver to strike head on side window, knocking driver unconscious.
07 - Other Non-Collision. Non-collision not captured in the listed non-collision options.
Example:
Damage to the vehicle produced by its own dislodged vehicle parts (including hood flying up and contacting the windshield).
16 - Thrown or Falling Object is used when any object (1) is thrown (intentionally or unintentionally) and impacts an in-transport vehicle, or (2) falls onto, into, or in the path of an in-transport motor vehicle. If a tree limb falls from a tree and is contacted by a car, select 16 - Thrown or Falling Object. If a person maliciously throws an object off an overpass into traffic below, select 16 - Thrown or Falling Object. This excludes contacts made by loads or objects set in-motion by a motor vehicle (see 54 - Motor Vehicle In-Transport Strikes or Is Struck by Cargo, Persons or Objects Set-in-Motion from/by Another Motor Vehicle In-Transport under the Collision with Motor Vehicle In-Transport section of this field).
44 - Pavement Surface Irregularity (Ruts, Potholes, Grates, etc.) is used when the pavement surface irregularity is on a roadway. If the impact is with a surface irregularity (e.g., ruts, potholes) not on a roadway select 58 - Ground.
51 - Jackknife (harmful to this vehicle) applies to a condition that occurs to an articulated vehicle, (any vehicle with a trailing unit(s) connected by a hitch; e.g., truck tractor or single-unit truck with one or more trailers, articulated bus, car pulling a boat on a trailer, etc.) while in motion. The condition reflects a loss of control of the vehicle by the driver in which the trailer(s) yaws from its normal straight-line path behind the power unit, striking the power unit, causing damage to the power unit or trailer. Jackknife should only be selected as a harmful event if there is clear indication of damage to the jackknifed vehicle or injury to its occupants caused by the jackknife.
72 - Cargo/Equipment Loss or Shift (harmful to this vehicle) refers specifically to the loss or shift of items carried on or in a motor vehicle or its trailing unit, and not to the vehicle or trailing unit itself. This option is only to be used when the injury- or damage-producing event in the crash is the loss or shift of cargo in/on a vehicle causing damage to that vehicle, or injury to its passengers/occupants. This option should never be selected to refer to a "collision" event (see 54 - Motor Vehicle In-Transport Strikes or is Struck by Cargo, Persons or Objects Set-in-Motion from/by Another Motor Vehicle In-Transport under the Collision with Motor Vehicle In-Transport section of this field).
Example: A pickup truck brakes rapidly to avoid a collision. This causes a piece of lumber in the pickup bed to smash through the rear window.
Collision with Motor Vehicle in Transport:
12 - Motor Vehicle In-Transport is used when the injury- or damage-producing event is two motor vehicles in-transport making contact within the trafficway boundaries. In-transport means that the motor vehicle is in-motion or on the roadway portion of a trafficway.13 - Not-In-Motion or Working Motor Vehicle is Struck by Motor Vehicle In-Transport is used when the injury- or damage-producing event is one not-in-motion (motor vehicle types 02 and 03) or working (motor vehicle type 04) motor vehicle being struck by a motor vehicle in-transport. In-transport means that the motor vehicle is in-motion or on the roadway portion of a trafficway.
54 - Motor Vehicle In-Transport Strikes or is Struck by Cargo, Persons or Objects Set-in-Motion from/by Another Motor Vehicle In-Transport is used when the injury- or damage-producing event is two motor vehicles in-transport making contact with something set-in-motion by one of the vehicles. In these circumstances, both vehicles should have this option selected in their SEQUENCE OF EVENTS field. In crashes involving harmful events caused by objects set-in-motion by a motor vehicle in-transport, remember that a vehicle’s load is considered part of the vehicle.
Examples:
- If cargo falls from a truck (in-transport) and strikes another motor vehicle in-transport, this is treated as a two-vehicle crash. Therefore, the proper option for both vehicles is 54 - Motor Vehicle In-Transport Strikes or is Struck by Cargo, Persons or Objects Set-in-Motion from/by Another Motor Vehicle In-Transport.
- If cargo falls from a truck (in-transport) and strikes another vehicle that is not in-transport, this is also treated as a two-vehicle crash; however in this example, the proper option is 14 - Parked Motor Vehicle or 45 - Working Motor Vehicle depending on which type of not in-transport vehicle was contacted by the load.
- If cargo falls from a truck (in-transport) and strikes a pedestrian, the proper option would be 08 - Pedestrian.
Example:
A vehicle loses control attempting to turn into a gas station and strikes another vehicle pulling away from the pump in the station lot.
Collision with Object Not Fixed:
08 - Pedestrian is used for all those not on a personal conveyance. A person pushing a vehicle should be considered a 08 - Pedestrian. A person being carried by another person should also be considered a 08 - Pedestrian.09 - Pedalcyclist is used for any person on a non-motorized other road vehicle propelled by pedaling. Examples include a bicycle, tricycle, unicycle or pedal car.
10 - Railway Vehicle is any land vehicle that is (1) designed primarily for, or in use for, moving persons or property from one place to another on rails and (2) not in use on a land way other than a railway.
11 - Live Animal is used for collisions with live animals (domesticated or wild) that are not themselves being used as transportation or to draw a wagon, cart or other transport device.

Please remember that if this event in the SEQUENCE OF EVENTS is a collision with a live animal then you will have to select the animal in the space provided (i.e., Bear – Brown, Bear – Black, Bear – Other/Unknown, Bison / Musk Ox, Cat / Dog, Caribou, Deer, Fox, Horse / Cow, Moose, Porcupine, Rabbit, Sheep / Goat, Squirrel, Wolf, etc.)
14 - Parked Motor Vehicle is used when the impact occurred between a motor vehicle in-transport and a motor vehicle neither on a roadway nor in motion. A vehicle stopped off the roadway, its door open over a roadway, is not in-transport.
15 - Non-Motorist on Personal Conveyance is used when the impact occurred between a motor vehicle in-transport and a pedestrian using a personal conveyance. A personal conveyance is a device, other than a transport device, used by a pedestrian for personal mobility assistance or recreation. These devices can be motorized or human powered, but not propelled by pedaling.
Inclusions:
|
Exclusions: - Golf carts - Low Speed Vehicles (LSVs) - Go-carts - Minibikes - "Pocket" motorcycles - Motor scooters - Mopeds |
45 - Working Motor Vehicle is used to indicate the motor vehicle contacted was in the act of performing construction, maintenance, or utility work related to the trafficway when it became an involved unit. This "work" may be located within open or closed portions of the trafficway and motor vehicles performing these activities can be within or outside the trafficway boundaries. This option does not include private construction/maintenance vehicles, or vehicles such as garbage trucks, delivery trucks, taxis, emergency vehicles, tow trucks, etc.
Examples:
- Asphalt/steam roller working in a highway construction zone paving the roadway or flattening dirt.
- State highway maintenance crew painting lane lines on the road, mowing grass on the roadside or median, repairing potholes, removing debris from the roadway, etc.
- Utility truck or a "cherry picker", performing maintenance on power lines along the roadway or maintaining a traffic signal.
- A private excavating company contracted by the State digging the foundation for a new overpass.
- A state, county, or privately owned snow plow, plowing ice/snow as part of a highway maintenance activity.
- Street sweeper sweeping the street.
- A vehicle in a mobile work convoy displaying arrow boards or other signaling devices warning motorists of the work activity.
- A law enforcement vehicle which is participating strictly in a stationary construction or mobile maintenance activity as a traffic slowing, control, signaling or calming influence.
Select 49 - Ridden Animal or Animal-Drawn Conveyance if the impact occurred between a motor vehicle in-transport and a ridden animal or an animal-drawn transport device. See 18 - Other Object (Not Fixed) for an animal carcass lying in the roadway.
Collision with Fixed Object
The options 58 - Ground, 33 - Curb, 34 - Ditch and 35 - Embankment are grouped under the Collision with Fixed Object subset because they represent harmful events in the crash (i.e., – they are associated with an impact that produces injury or damage). If there is no indication of damage from contact with the fixed object (e.g., "came to rest on the embankment" or "ran into the ditch"), then it is not included in the SEQUENCE OF EVENTS.17 - Boulder is a rock of sufficient mass that when struck by a motor vehicle moves very little and remains basically intact. It may be considered as a fixed object.
19 - Building is used when the vehicle impacts a roofed and walled structure built for permanent use. The type of construction material used is not of interest, nor is the use of the building.
20 - Impact Attenuator/Crash Cushion is a device for controlling the absorption of energy released during vehicle collision (crash cushion). Its most common application involves the protection of fixed roadside objects such as bridge piers, elevated gores at exit ramps, etc. Examples include barrels filled with water or sand, and plastic collapsible structures.
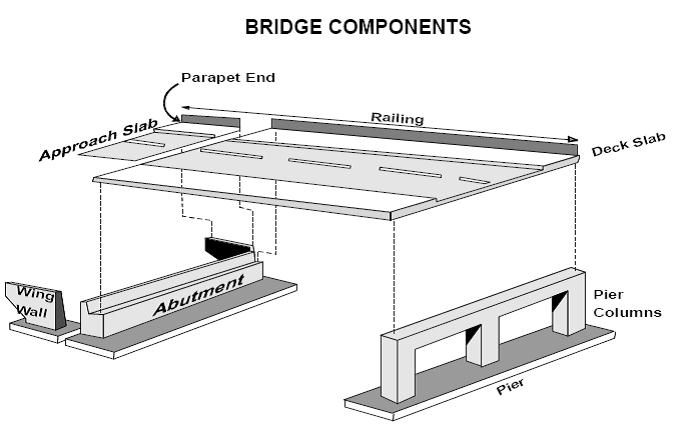
21 - Bridge Pier or Support is a square or round column of stone, concrete, brick, steel or wood for supporting a bridge between abutments. This option includes the bridge abutments which are supporting the ends of a bridge. Abutments are generally designed for retaining or supporting the embankment under bridge ends and composed of stone, concrete, brick or wood (includes the wing-walls).
23 - Bridge Rail (Includes Parapet) is a wooden, brick, stone, concrete or metal fence-like structure which runs along the outermost edge of the roadway or sidewalk on the bridge or a rail constructed along the top of a parapet. Balustrade is often used synonymously with parapet.
- Bridges do not need to support another roadway. It may be an overpass for a train or even for a viaduct (water conduit).
24 - Guardrail Face is a low barrier that has the primary longitudinal structure composed of metal (plates, mesh, box beam, etc.). A guardrail is differentiated from 25 - Concrete Traffic Barrier by the material making up the greatest part of the longitudinal portion of the structure. In the case of guardrails, this is metal whereas in concrete barriers this is concrete (including concrete rails).
Guardrails, which serve as bridge rails, should be considered 23 - Bridge Rails (Includes Parapet).
25 - Concrete Traffic Barrier refers to the longitudinal traffic barriers constructed of concrete. This includes all temporary concrete barriers regardless of location (e.g., temporary Jersey Barrier on a bridge being used to control traffic during bridge repair/construction). Concrete walls (vertical side surfaces) do not apply here; see 39 - Wall. 26 - Other Traffic Barrier is used for all other longitudinal barriers such as wood or rock and unknown barrier composition type.
30 - Utility Pole/Light Support refers to supports for highway lighting systems, not including other private lighting systems (e.g., parking lot lights). 30 - Utility Pole/Light Support is used for electrical, telephone, cable & other utility pole-type supports.
31 - Other Post, Other Pole or Other Supports is used for posts other than highway signs (e.g., reflectors on poles alongside of roadway, parking meters, flag poles, etc.). For mail box posts, use 53 - Mail Box.
32 - Culvert is a man-made drain or channel crossing under a road, sidewalk, etc.
33 - Curb is a concrete or asphalt structure that borders the roadway. It provides drainage control and pavement edge delineation. The face of the curb may be sloped or vertical.
34 - Ditch includes any man-made structure for drainage purposes. A ditch ends where a culvert begins and resumes on the opposite side of the culvert.
35 - Embankment is a raised structure to carry a roadway, to hold back water, or the result of excavation or washout (including erosion) which may be faced with earth (or rock, stone or concrete).
A 35 - Embankment can usually be differentiated from a 39 - Wall by its incline whereas a wall is usually vertical. However, there are exceptions to this; such as a retaining wall that may be inclined or a vertical embankment that is caused by a natural event such as a washout. In crashes involving a field approach or crossing, if in doubt about when to use 32 - Culvert, 34 - Ditch or 35 - Embankment use the following criteria:
- Use 34 - Ditch if the driver would not have been able to recover from the ditch even if there had been no field approach (crossing).
- Use 35 - Embankment if the driver would have been able to recover from the ditch, but struck the field approach (crossing) prior to doing so.
- Use 35 - Embankment if it is not known whether or not the driver would have been able to recover from the ditch and a field approach (crossing) is involved.
39 - Wall is a primarily vertical structure composed of concrete, metal, timber or stone which is not part of a building or a fence but typically is used for retaining earth, abating noise, and separating areas (but not for containment as in the primary function of a fence). Also included as a 39 - Wall are headwalls (or endwalls) that are sometimes provided on culvert ends principally to protect the sides of the embankment around the culvert opening against erosion. This does not include wing-walls, which are attached to ends of bridge abutments and extend back at an angle from the roadway. Wing-walls should be considered 21 - Bridge Pier or Support.
40 - Fire Hydrant refers to the roadside device used by fire departments to provide water for fighting fires. Usually made of steel, these devices are also referred to as fire plugs or fire stand pipes in some areas.
41 - Shrubbery refers to vegetation which is usually of a woody multi-stemmed variety and in most instances is low growing rather than tall. May also be called bushes. Some common examples are boxwood, hawthorn, and mountain laurel.
42 - Tree (Standing Only) is used when a vehicle strikes a standing tree. This includes impacts from overhanging branches or tree stumps. If a vehicle strikes a tree lying in the roadway, use 18 - Other Object (Not Fixed). If a tree falls on a vehicle as it is passing by, use 16 - Thrown or Falling Object.
43 - Other Fixed Object is used when the object is fixed (considered a permanent structure) and is not described by any of the other fixed object options.
Examples:
- Bus shelters
- Pedestrian walkways
- Toll booths
- Guy wires supporting utility poles
- U. S. Mailbox for public use
48 - Snow Bank is used when snowfall and/or road plowing creates essentially fixed barriers of snow/ice which are not snow-covered earth or rock embankments.
50 - Bridge Overhead Structure is used when striking the bottom of a bridge while traveling on a trafficway underneath it.
52 - Guardrail End is selected if a vehicle strikes the end of a guardrail. Guardrails can have a separate flat or rounded piece of metal attached to the end of an expanse of guardrail face.
53 - Mail Box refers to a private residence mail/newspaper box including the post. A cluster of private mailboxes is included in this option. This option does not include U.S. Mailbox, which are typically blue and are for general public use. Select a U.S. Mailbox as 43 - Other Fixed Object.
57 - Cable Barrier refers to a flexible barrier system which uses several cables typically supported by steel posts. These barriers are designed to help lessen impact or keep vehicles within the confines of the road.
58 - Ground is used when the impact is with an earthen or paved surface off of the roadway. 58 - Ground is not to be entered when the harmful event is 01 – Rollover/Overturn.
59 - Traffic Sign Support is used when the post supporting a traffic sign, or the sign itself, is hit by a motor vehicle in-transport. This includes mile marker posts and signs above the trafficway.
99 - Unknown is used when the most harmful event is not known.
Non-Harmful Events:
60 - Cargo/Equipment Loss or Shift (non-harmful) refers specifically to the loss or shift of items carried on or in a motor vehicle or its trailing unit, and not to the vehicle or trailing unit itself. This option should never be used to refer to:- a "collision" event (see 54 - Motor Vehicle In-Transport Strikes or is Struck by Cargo, Persons or Objects Set-in-Motion from/by Another Motor Vehicle In-Transport)
- a harmful event related to the loss or shift of cargo in/on a vehicle causing damage to that vehicle, or injury to its occupants (see 72 - Cargo/Equipment Loss or Shift (harmful to this vehicle)).
A load of logs on a tractor/semi-trailer shifts as the truck rounds a curve resulting in an overturn.
61 - Equipment Failure (blown tire (non-harmful), brake failure, etc.) Examples of equipment failure include blown tires, brake failures, etc.
62 - Separation of Units is used when a trailing unit separates from its power unit or another trailing unit(s). This applies to truck tractors with trailer(s), single-unit trucks with a trailer and other vehicles pulling a trailer (e.g., car pulling a boat or motor home).
63 - Ran Off Roadway-Right is used if the vehicle runs off the right side of the roadway. This option can be used anytime in the event sequence before or after any harmful event.
64 - Ran Off Roadway-Left is used if the vehicle runs off the left side of the roadway. This option can be used anytime in the event sequence before or after any harmful event.
Guideline for Running Off Road on Divided Highways:
On a divided highway, a vehicle can run off the roadway by leaving the roadway and entering the median. When this occurs, the proper "Ran Off Roadway" option is always 64 - Ran Off Roadway-Left. 64 - Ran Off Roadway - Left will also apply in situations where the vehicle traverses the median and continues across and exits the opposing roadway.
65 - Cross Median is used when a vehicle departs its roadway and traverses the median and enters the shoulder or travel lanes on the opposite side of a divided highway.
66 - Downhill Runaway refers to any vehicle that cannot decelerate on a downhill grade.
67 - Vehicle Went Airborne select this option if the vehicle left the ground (excludes rollover). Examples: the vehicle drove off a cliff, the vehicle was launched into the air after striking another vehicle or after traversing a berm.
68 - Cross Centerline is used when a vehicle crosses over the centerline of a two-way, undivided highway. The centerline must be delineated with paint or raised markers. This also includes unstabilized situations (see definition for unstabilized situation in Appendix C) involving vehicles completely crossing over a continuous left turn lane.
69 - Re-entering Roadway is used when a vehicle that departed the roadway portion of the trafficway returns to the same roadway (e.g., a motor vehicle in-transport runs off the roadway right, strikes the guardrail face, then re-enters the roadway and collides with another motor vehicle in-transport).
70 - Jackknife (non-harmful) applies to a condition that occurs to an articulated vehicle, (any vehicle with a trailing unit(s) connected by a hitch; e.g., truck tractor or single-unit truck with one or more trailers, articulated bus, car pulling a boat on a trailer, etc.) while in motion. The condition reflects a loss of control of the vehicle by the driver in which the trailer(s) yaws from its normal straight-line path behind the power unit.
71 - Vehicle Set in Motion applies to a vehicle that is set in motion accidently or otherwise by an occupant or other circumstances (e.g., small child puts vehicle in gear while driver is out of vehicle, vehicle slides down ice covered driveway into roadway while driver is not in vehicle.)